Introduction
In today’s digital era, Machine Learning (ML) has become a technology that quietly powers almost every digital service we use. Whether it’s Netflix recommending the perfect movie, YouTube showing you trending videos, Amazon suggesting products, or Google Maps guiding you on the fastest route—Machine Learning applications power all of these.
But here comes the big question:
What is Machine Learning?
Is it something only coders and data scientists can understand, or can a non-technical person also grasp it?
The answer is: Machine Learning is not rocket science for beginners—if explained in a simple and human-friendly way. And that’s exactly what we’ll do in this blog.
Here’s what you’ll learn today:
- What is Machine Learning (ML)?
- History of Machine Learning (how it started & evolved).
- Types of ML (Supervised, Unsupervised, Reinforcement).
- Real-world applications of ML.
- Challenges & limitations.
- Future scope of ML.
- FAQs that beginners always ask.
1. What is Machine Learning?
At its core, Machine Learning is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) where computers are trained to “learn from data” instead of being explicitly programmed.
In simple terms, a computer learns from past experiences and improves over time.Just like humans learn from practice, machines learn from data patterns.
Real-Life Example:
When you watch a travel vlog on YouTube, the next day, YouTube suggests more travel-related videos. No one is manually programming those suggestions. Instead, YouTube’s ML algorithms learn from your viewing history and predict what you may like next.
That’s why ML is often called “data-driven learning”.Here is what is Machine Learning in short words.
2. A Brief History of Machine Learning
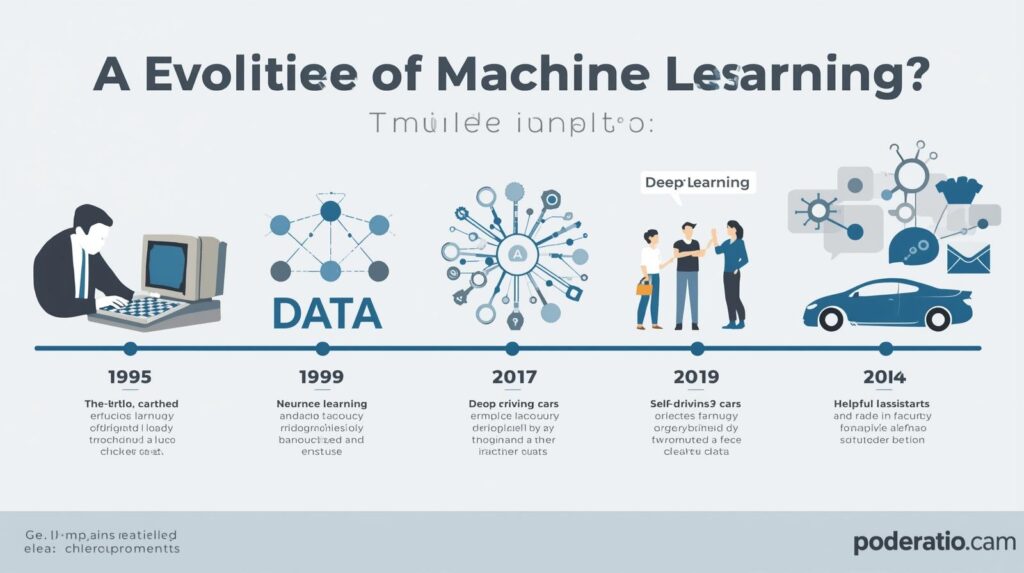
Machine Learning might feel like a modern concept, but its roots go back decades.
- 1950s: The Birth of the Idea
- Alan Turing introduced the concept of machines that could “think” in his paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” (1950). Arthur Samuel (1952) developed the first computer program that could play checkers and improve by learning from experience.
- 1960s–70s: Early Experiments
- Researchers built simple neural networks and experimented with algorithms that could recognize patterns—the lack of computing power limited progress.
- 1980s: Rise of Algorithms
- The development of Decision Trees, Neural Networks (backpropagation), and Expert Systems gave ML a boost.
- 1990s: The Data Era
- With more digital data, ML shifted from theory to practice. Spam filters, handwriting recognition, and stock predictions emerged.
- 2000s: The Big Boom
- The internet brought Big Data. Companies like Google, Amazon, and Netflix started applying ML for recommendations, ads, and personalization.
- 2010s–Present: Deep Learning Revolution
- Deep Learning made image recognition, voice assistants, translation, and self-driving cars possible. Every day, apps like Google Photos, Siri, Alexa, and ChatGPT rely on ML.
Today, ML is not just research—it’s a billion-dollar industry changing healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment.
3. Types of Machine Learning
There are three main types of Machine Learning easy to understand: What is Machine Learning :
Supervised Learning
In this, the machine is given both data and correct answers (labels). It learns the relationship between input and output and predicts results for new data.
Example: Email spam filter.
Real-life: Credit card fraud detection.
Unsupervised Learning
The machine is given only raw data without answers. It identifies patterns and groups.
Example: Shopping app recommendations.
Real-life: Market segmentation for businesses.
Reinforcement Learning
The machine learns through trial and error. It receives rewards or punishments based on actions and improves over time.
Example: Teaching a computer to play chess.
Real-life: Self-driving cars, Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo.
4. Why is Machine Learning Important?
The importance of ML is huge because it is transforming industries:
- Handles Big Data – The more data, the better the predictions.
- Faster Decisions – ML processes data quickly than humans.
- Automation – Chatbots, customer support, and data entry.
- Accuracy – Detecting fraud, predicting diseases.
- Innovation – Creating new solutions in every sector.
Example: Banks save billions by detecting fraud in real-time with ML.
5. Real-Life Applications of Machine Learning
- Healthcare: Diagnosing diseases from X-rays and MRI.
- Finance: Detecting fraud, algorithmic trading.
- Retail/E-commerce: Product recommendations.
- Transportation: Tesla Autopilot, Uber surge pricing.
- Education: Personalized apps like Byju’s, Duolingo.
- Entertainment: Netflix, YouTube, Spotify recommendations.
- Social Media: Instagram filters, Facebook friend suggestions.
6. Case Studies
- Netflix Recommendation System
- Netflix analyzes billions of watch hours with ML. Around 80% of what users watch comes from recommendations. It saves Netflix about $1 billion annually.
- Amazon Product Recommendations
- Amazon uses ML for personalized suggestions, which generate over 35% of its revenue.
- IBM Watson in Healthcare
- IBM Watson analyzes patient history and medical journals to recommend personalized treatments. It helps doctors with accurate cancer diagnoses.
- Tesla Self-Driving Cars
- Tesla uses ML and computer vision to collect data from every mile driven. Reinforcement learning improves its autopilot system continuously.
7. Challenges in Machine Learning
Despite its success, ML faces challenges:
- Data Dependency: Requires massive clean datasets.
- Bias: Poor or biased data creates unfair results.
- Explainability: Many ML models are “black boxes”.
- Cost: Training large models is expensive.
- Privacy: Collecting user data raises ethical concerns.
8. Future of Machine Learning
- The future of Machine Learning looks incredibly promising. Over the next 5–10 years, ML is expected to reshape industries, improve human lives, and open new opportunities. Let’s explore what lies ahead:
- Smarter Healthcare
ML will assist doctors in early disease detection, personalized medicine, and even AI-assisted surgeries. For example, cancer could be detected in its earliest stage with higher accuracy than ever before. - Fully Autonomous Cars
Companies like Tesla, Google’s Waymo, and Uber are investing heavily in self-driving vehicles. Within the next decade, self-driving taxis and trucks could become normal in big cities, reducing accidents caused by human error. - AI in Education
Personalized learning platforms will become more advanced. Instead of a “one-size-fits-all” syllabus, ML will design custom study paths for every student, identifying strengths and weaknesses. - AI + Robotics
Robots powered by ML will play a major role in industries like manufacturing, logistics, and even household services. Imagine robots that learn new tasks in real-time just like humans. - Natural Language Processing (NLP) Improvements
Tools like ChatGPT are only the beginning. In the future, AI will understand languages, accents, and emotions even better, making communication with machines as natural as talking to humans. - Climate Change Solutions
ML will help scientists predict natural disasters, optimize energy usage, and design eco-friendly solutions. From smart agriculture to renewable energy grids, ML will play a key role in sustainability. - Cybersecurity and Fraud Detection
With growing digital transactions, ML will be crucial in detecting suspicious activities in real time and protecting users from cyberattacks. - AI for Creativity
Music, art, writing, filmmaking—ML will collaborate with humans to create new forms of entertainment and innovation. Already, we see AI generating music, stories, and even movies. - Everyday Personal Assistants
The future of Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant will be far more intelligent. They won’t just answer questions but anticipate needs—like booking a doctor’s appointment when your health data suggests you need one. - Global Market Growth
According to experts, the global Machine Learning market is projected to exceed $200+ billion by 2030, making it one of the fastest-growing industries in the world. to surpass $200 billion by 2030.
9. FAQs About Machine Learning
Q1. What is Machine Learning in simple words?
It’s when a computer learns from data and improves without re-programming.
Q2. Is ML the same as AI?
No. AI is the broader field, ML is a subfield.
Q3. What are the types of ML?
Supervised, Unsupervised, Reinforcement.
Q4. Where is ML used?
Healthcare, finance, e-commerce, entertainment, transportation.
Q5. Best programming languages for ML?
Python, R, Julia, Java.
Q6. Is a career in ML secure?
Yes, ML/AI jobs are growing fast.
Q7. What’s the difference between ML and Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is a specialized type of ML using neural networks.
Conclusion
Now you should have a clear idea of what is Machine Learning, how it started, its types, applications, challenges, and future scope.
From Netflix recommendations to Tesla’s self-driving cars, ML is making life easier and creating new opportunities. In the future, it will become even more powerful and accessible.
If you want to build a career in technology, Machine Learning is a future-proof skill.
Question for you: Which ML application excites you the most—Netflix’s recommendation system, Tesla’s self-driving cars, or IBM Watson in healthcare?